Glaucoma
Symptoms Of Glaucoma
- Mostly no symptom - diagnosed on routine examination.
- Mild headache, discomfort around eyes.
- Blurring of side vision.
- Frequent changes in glass prescription.
- By the time patient notices decrease in vision due to glaucoma, most of the optic nerve is damaged that is why it is called silent thief of sight.
Risk factors for glaucoma
- Age factor – The incidence is more after 40 years of age and increases with every passing decade
- High intraocular pressure
- Family History of glaucoma - in parents & siblings
- Diabetes, hypertension, Myopia
- Using Steroids drops over a long period of time or patients on oral steroids.
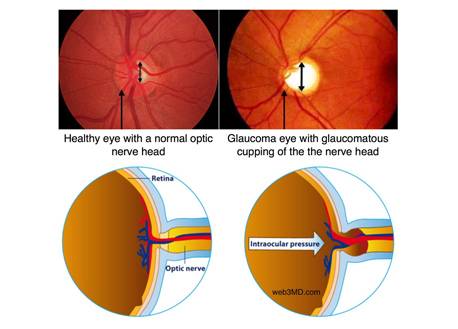
How is glaucoma diagnosed?
Glaucoma can be diagnosed with a routine examination or when a patient visits the doctor for the above-described symptoms.
Diagnose is confirmed by:
- Tonometry/eye pressure checkup: Normal eye pressure is 12-21 mm Hg. A rise in intraocular pressure is the highest risk factor for glaucoma.
- Optic nerve examination: By a special lens to check the nerve loss
- Pachymeter: Corneal thickness measurement to checkup for corrected intraocular pressure.
- Perimetry or computerized visual field testing: To check the subtle defect in field of vision which we are not aware of in routine day today life.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): A kind of scan of the optic nerve to evaluate nerve fibre layer thickness and also presence and extent of glaucoma damage.
- Fundus Photography: The photography of the optic nerve to check for progression or stability of glaucoma.
